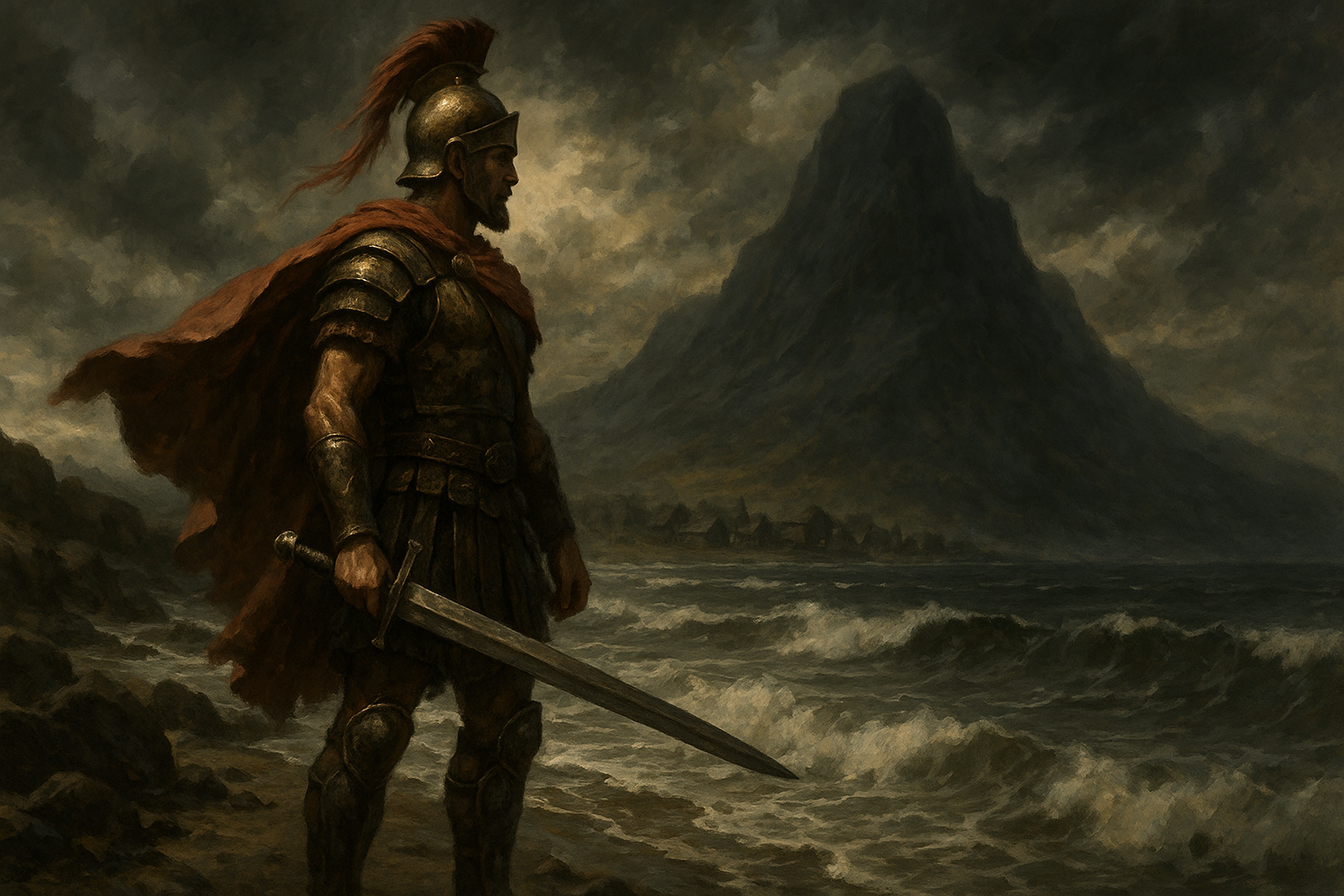
Heroism in Beowulf: The Quintessential Anglo-Saxon Epic
In 'Beowulf', heroism is not just about physical prowess but also about legacy, loyalty, and the burdens that come with great power. Beowulf’s journey exemplifies the qualities that define a true hero, showcasing bravery in the face of insurmountable odds and the complexities of fate.